Amino Acid Analysis:
Amino Acid Analysis (AAA) is a precise method for quantifying amino acid composition in proteins, peptides, and biological samples.
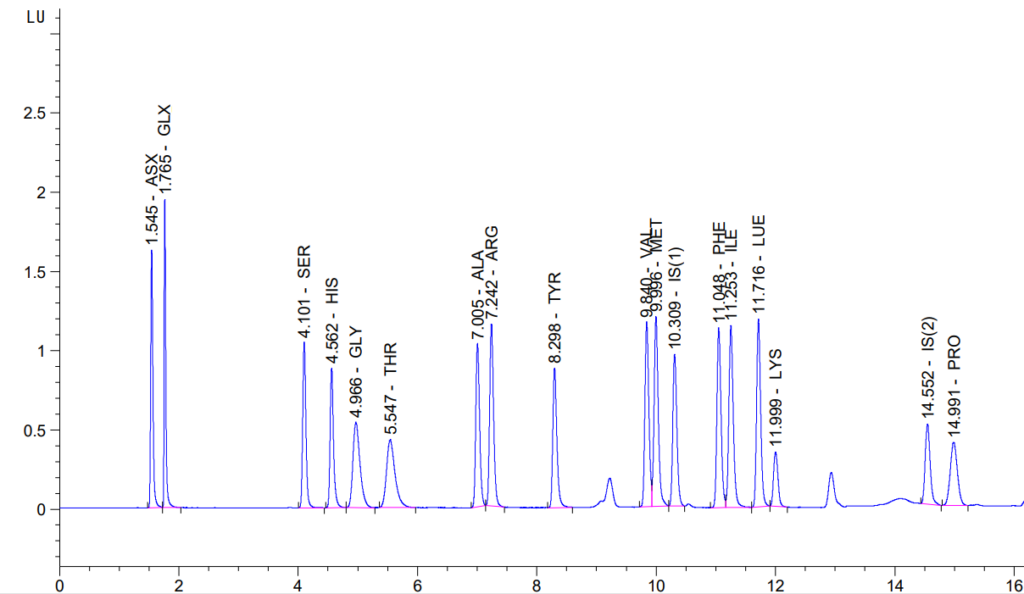
Proteins and peptides are hydrolyzed to their constituent amino acids, separated by HPLC, and detected by UV or fluorescence.
For free amino acids (e.g., in serum, cerebrospinal fluid, or culture media), hydrolysis is omitted after removing proteins and peptides by filtration.
AAA is the gold standard for protein and peptide quantification far more accurate than colorimetric assays (e.g., Bradford or BCA) and an essential tool for protein quality control, composition verification, and metabolic or nutritional studies.
Applications
- Quantification and qualification of recombinant proteins and peptides
- Peptide synthesis validation (mole percent comparison to theoretical sequence)
- Monitoring amino acid changes in cell culture media, serum, or plant tissues
- Resin and drug loading quantitation on nanoparticles
- Assessing enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency in dipeptide libraries
- Environmental and feed analysis for total amino acid composition
Contact:
For consultation, special assays (Cys, Trp, or unusual amino acids), or project planning:
pcl@ag.tamu.edu
Protein Chemistry Laboratory, Texas A&M University

Sample Submission
Packaging
- Use screw cap microtubes with gaskets (preferred) or securely sealed Eppendorf tubes
- Cushion samples for shipping (e.g., FedEx) to prevent cap loosening
- Cooling optional biological activity preservation not required
Sample Amount & Concentration
- Submit 30–50 µg total sample (3 × 10-15 µg replicates)
- Ideal concentration: 0.5–2 mg/mL
- Matrix: water preferred
- Avoid TRIS, glycerol, high salt, lipids, or sugars
Documentation
- Notify us before shipping at pcl@ag.tamu.edu
- Include the Amino Acid Analysis Sample Submittal Form (available on this site)
- Print and ship the form with your sample
Sample Types & Methods
Proteins & Peptides
- Vapor-phase acid hydrolysis (6 N HCl, 150 °C, 1.5 h under argon)
- Suitable for purified proteins and peptides
- Reports 16 amino acids (Asn/Gln as ASX/GLX)
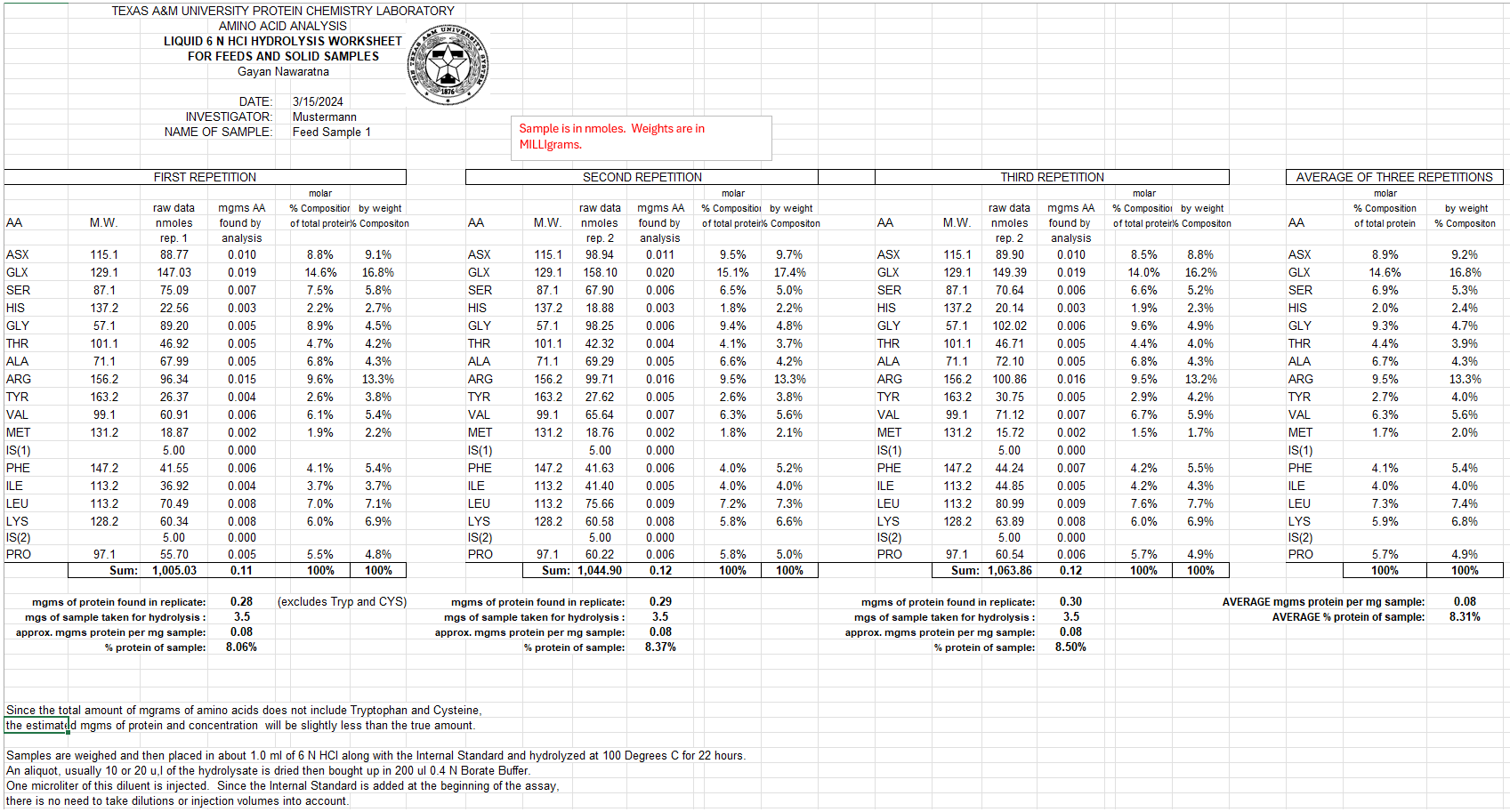
2. Solid or Feed Samples
- Liquid-phase hydrolysis (6 N HCl, 100 °C, 22 h)
- Cysteine and Tryptophan not preserved
3. Physiological Samples / Free Amino Acids
- Proteins removed using a 5 kDa MWCO filter or acid precipitation
- No hydrolysis required
- Suitable for Glutamine, Asparagine, Citrulline, β-Alanine, Taurine, Ornithine, etc.
Reported Amino Acids
- Standard assay: 16 amino acids
- Asparagine/Glutamine → reported as ASX/GLX
- Cysteine quantifiable only with pre-alkylation (separate assay)
- Tryptophan requires methanesulfonic acid hydrolysis (separate assay, larger sample)
- Physiological assays: up to 19 amino acids, with optional additions (Cit, β-Ala, Taur, Orn)
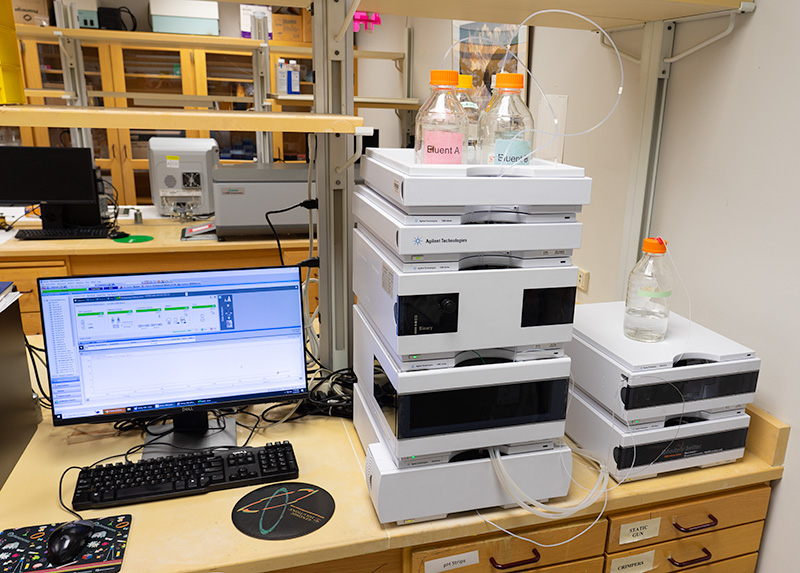
Instrumentation
- Hydrolysis: PicoTag Workstation under argon
- HPLC System: Agilent 1260 Infinity with OpenLab software
- Derivatization: Pre-column using OPA (primary AAs) and FMOC (secondary AAs)
- Column: 2.1 × 200 mm Hypersil AA-ODS (5 µm)
- Detection: UV: 338/390 nm (OPA), 266/324 nm (FMOC) and Fluorescence: 340/450 nm and 266/305 nm
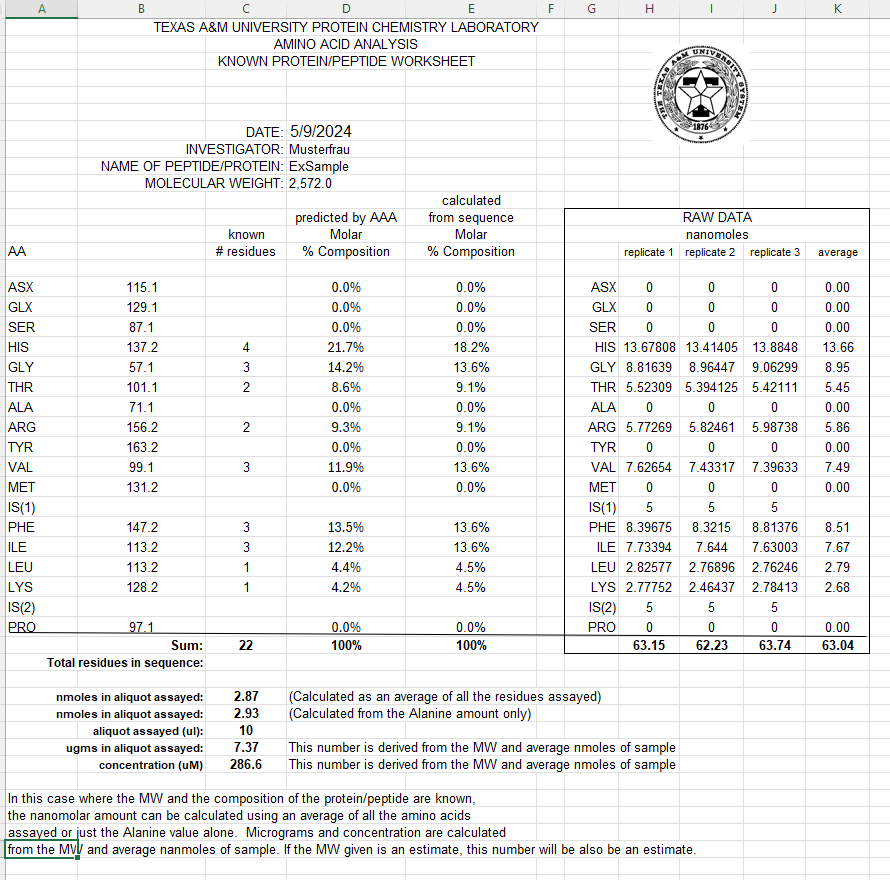
Results & Data
Results provided as an Excel workbook, including:
- Calculated sample amount and molar composition (if MW provided)
- Replicate averages
- Percent amino acid composition
Data retention:
- Raw data -2 years
- Processed summaries -5 years
Notes
- Hydrolysis deamidates Asn/Gln (reported as ASX/GLX) and destroys Trp (requires separate assay).
- Cysteine can be preserved with alkylation before hydrolysis (optional add-on).
- Complex matrices (e.g., serum, media) may yield combined hydrolysis and free amino acid signals.
Amino Acid Codes
| Amino Acid | Three letter Code | One letter Code |
| Alanine | Ala | A |
| Cysteine | Cys | C |
| Aspartic Acid | Asp | D |
| Glutamic Acid | Glu | E |
| Phenylalanine | Phe | F |
| Glycine | Gly | G |
| Histidine | His | H |
| Isoleucine | Ile | I |
| Lysine | Lys | K |
| Leucine | Leu | L |
| Methionine | Met | M |
| Asparagine | Asn | N |
| Proline | Pro | P |
| Glutamine | Gln | Q |
| Arginine | Arg | R |
| Serine | Ser | S |
| Threonine | Thr | T |
| Valine | Val | V |
| Tryptophan | Trp | W |
| Tyrosonine | Tyr | Y |
| Citrulline | Cit | |
| Hydroxyproline | Hyp | |
| Ornithine | Orn | |
| B-Alanine | B-Ala | |
| Asparagine/Aspartic Acid | Asx | B |
| Glutamine/Glutamic Acid | Glx | Z |
cannot be differentiated. Therefore, the resulting mixtures are designated as Asx and Glx.
